
Incoterms are terms used in international sales contracts that define the responsibilities and transfer of obligations between exporters and importers during the transportation of goods.
Incoterms were first published in 1936 by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) to prevent confusion regarding responsibilities in international trade. Over time, they have been regularly revised to reflect changes in global trade. The latest version in use today is “Incoterms 2020.”
According to the 2020 version, there are 11 Incoterms categorized under four main groups. Below, you can find explanations of each Incoterm and a table summarizing the buyer’s and seller’s responsibilities.
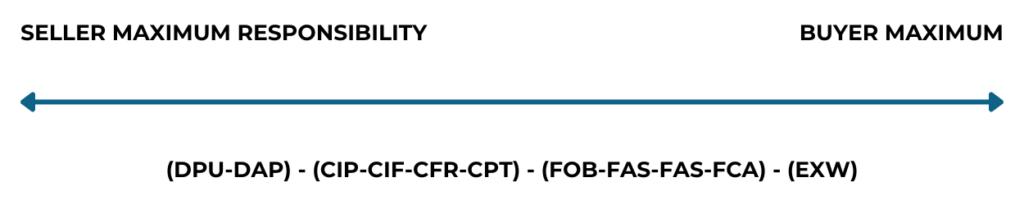
| Delivery Terms | Mode of Transport | Packaging & Loading | Inland Transport in Export Country | Export Customs | Loading onto Main Carrier | Main Transport Responsibility | Freight | Insurance | Unloading from Main Carrier | Import Customs | Inland Transport in Import Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EXW | Multimodal | Seller | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer | Not Mandatory | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer |
| FCA | Multimodal | Seller | Seller | Seller | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer | Not Mandatory | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer |
| FAS | Sea | Seller | Seller | Seller | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer | Not Mandatory | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer |
| FOB | Sea | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Buyer | Buyer | Not Mandatory | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer |
| CPT | Multimodal | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Buyer | Seller | Not Mandatory | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer |
| CFR | Sea | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Buyer | Seller | Not Mandatory | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer |
| CIF | Sea | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Buyer | Seller | Seller | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer |
| CIP | Multimodal | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Buyer | Seller | Seller | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer |
| DAP | Multimodal | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Not Mandatory | Buyer | Buyer | Buyer |
| DPU | Multimodal | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Not Mandatory | Seller | Buyer | Buyer |
| DDP | Multimodal | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Seller | Not Mandatory | Seller | Seller | Seller |
1. EXW (Ex Works) – Delivery at Factory
The seller makes the goods available at their premises or a designated location.
Seller’s responsibilities: Prepare the goods for collection and notify the buyer.
Buyer’s responsibilities: Handle loading, transportation, customs clearance, and all related costs.
Risk transfer: When the seller makes the goods available at the designated place.
2. FCA (Free Carrier) – Delivery to Carrier
The seller delivers the goods to the carrier or another location designated by the buyer.
Seller’s responsibilities: Transport and hand over the goods to the carrier.
Buyer’s responsibilities: Organize transportation, customs clearance, and additional costs.
Risk transfer: When the goods are delivered to the carrier.
3. FAS (Free Alongside Ship) – Delivery Alongside Ship
The seller delivers the goods alongside the ship at the port.
Seller’s responsibilities: Transport the goods to the port and place them alongside the ship.
Buyer’s responsibilities: Handle loading, transportation, customs clearance, and costs.
Risk transfer: When the goods are placed alongside the ship.
4. FOB (Free on Board) – Delivery on Board the Ship
The seller loads the goods onto the ship and hands over responsibility.
Seller’s responsibilities: Transport goods to the port and load them onto the ship.
Buyer’s responsibilities: Handle transport, customs clearance at destination, and related costs.
Risk transfer: When the goods are fully loaded onto the ship.
5. CPT (Carriage Paid To) – Transport Costs Paid
The seller pays for transportation, but the risk transfers when the goods are handed to the carrier.
Seller’s responsibilities: Deliver goods to the carrier and cover transportation costs.
Buyer’s responsibilities: Handle customs clearance at the destination and additional charges.
Risk transfer: When the goods are handed over to the carrier.
6. CFR (Cost and Freight) – Cost & Freight Paid
The seller covers product and freight costs, but the risk transfers when goods are loaded onto the ship.
Seller’s responsibilities: Load goods onto the ship and pay freight charges.
Buyer’s responsibilities: Handle customs clearance at the destination and additional costs.
Risk transfer: When goods are loaded onto the ship.
7. CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) – Cost, Insurance & Freight Paid
Similar to CFR, but the seller also provides basic transport insurance.
Seller’s responsibilities: Load goods onto the ship, pay freight, and provide insurance.
Buyer’s responsibilities: Handle customs clearance and additional costs.
Risk transfer: When goods are loaded onto the ship.
8. CIP (Carriage and Insurance Paid To) – Transport & Insurance Paid
The seller has the same obligations as CPT but must also provide insurance for transit risks.
Seller’s responsibilities: Deliver goods to the carrier, pay transport and insurance costs.
Buyer’s responsibilities: Handle customs clearance and destination charges.
Risk transfer: When the goods are handed over to the carrier.
9. DAP (Delivered at Place) – Delivered to Agreed Location
The seller transports the goods to the agreed-upon destination.
Seller’s responsibilities: Covers all transport costs and risks until arrival.
Buyer’s responsibilities: Handles unloading and customs clearance.
Risk transfer: When goods arrive at the designated location.
10. DPU (Delivered at Place Unloaded) – Unloaded at Agreed Location
The seller transports the goods and unloads them at the destination.
Seller’s responsibilities: Covers transport and unloading costs and risks.
Buyer’s responsibilities: Handles customs clearance and post-delivery arrangements.
Risk transfer: When goods are unloaded at the agreed location.
11. DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) – Duties & Taxes Paid
The seller assumes all costs and risks, delivering the goods to the buyer’s location, including customs duties.
Seller’s responsibilities: Covers transport, unloading, import duties, and customs clearance.
Buyer’s responsibilities: Accepts the goods upon arrival.
Risk transfer: When the goods are delivered at the agreed location.
